The Mediterranean coast has been facing significant challenges due to uncontrolled construction, population growth, and a massive increase in tourism. These pressures have jeopardized environmental security and access to vital natural resources, such as Water, Energy, Food, and Ecosystems.
According to scientific data and evidence, climate variability will impact communities living close to the shores. At the same time freshwater ecosystems such as groundwater-related coastal wetlands as well as coastal aquifers, are significantly contaminated, subject to unregulated exploitation and lack specific management frameworks as well as laws and/or policies for their protection. Under the Barcelona Convention, the Protocol on Integrated Coastal Zone Management provides the legal framework for the integrated management of the Mediterranean coastal zone.
The “Mediterranean Coastal Zones: Water Security, Climate Resilience and Habitat Protection” (CP 2.1 of the MedProgramme) aims at improving water security, human and ecosystem health, and climate resilience in Mediterranean coastal hot spots. It is executed jointly by UN Environment/MAP and two of its RACs (PAP/RAC and Plan Bleu/RAC), UNESCO-IHP and GWP-Med. The project’s goal is to strengthen and expand Integrated Zone Management in the Mediterranean region and enhance sustainability of services provided by coastal aquifers and their related habitats.
Activities are structured around two Components
Component 1: Coastal Zone Management
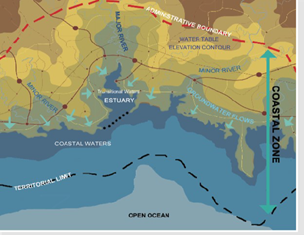
The aim of this Component is to promote coastal zone sustainability in beneficiary countries through the compliance with the ICZM Protocol and the adoption of national ICZM strategies, coastal plans and instruments, and improved gender equality. The Component supports the implementation of comprehensive ICZM approaches, including:
The coastal zone showing the ICZM Protocol boundaries,groundwaters and waters defined by the Water Framework Directive (WFD) (Credit: Brian Shipman, PAP/RAC)
- Preparation, adoption and support of gender sensitive National ICZM Strategies, or coastal plans, marine spatial plans and plans focused on coastal resilience to Climate Variability and Change, adopting the Integrative Methodological Framework (IMF) for Lebanon, Egypt and Morocco*
- Translation of intrinsic environmental vulnerabilities (ecosystems, climate, and groundwater) into Coastal Zone Use Capability or suitability maps and related guidance;
- Use of ICZM tools and instruments;
- Capacity building activities for ICZM, MSP and adaptation to climate variability and change (all project countries).
Activities under this Component extend from basin/aquifers, coastal and marine zones. Out of these, GWP-Med is contributing to the preparation of the Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM) Strategy for Lebanon and the ICZM Plan-Schema Regional du Littoral for the Moroccan Region of Tanger-Tetouan-Al Hoceïma (TTA) - through its efforts to integrate the results of the Water-Energy-Food-Ecosystem (WEFE) Nexus approach in the above processes and resulting documents.
Component 2: Management of Coastal Aquifers and Related Ecosystems
This Component aims at implementing sustainable management policies and practices in five coastal aquifers considered of priority importance by the beneficiary countries and in the coastal ecosystems related to them, while conducting sub-regional trainings and national dialogues on conjunctive surface and groundwater management solutions in coastal areas. To this end, a set of activities are implemented in five aquifers in Albania & Montenegro, Egypt, Lebanon, Morocco and Tunisia.
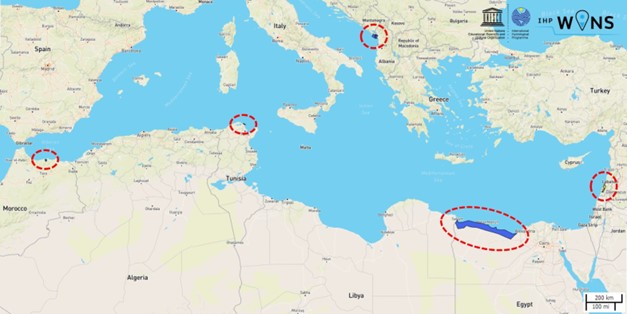
Location of the five priority aquifers for Component 2 of Child Project 2.1 (UNESCO-IHP 2015)
This Project is expected to:
- Enhance coastal zone sustainability in beneficiary countries through the expanded compliance with the ICZM Protocol and the adoption of national ICZM strategies, coastal plans and instruments, and improved gender equality.
- Increase resilience to climatic variability and change, and enhance water security of coastal populations through improved sustainability of services provided by coastal aquifers and by groundwater-related coastal habitats.
*In the remaining six countries of the project, activities supporting ratification and implementation of the ICZM Protocol, including awareness raising and capacity building activities will be implemented.
