/ Southern Africa
Partners to Advance Sustainable Financing Solutions for shared Transboundary Resources in Southern Africa
2025: The Southern African Development Community (SADC) will convene representatives from its Member States, River Basin Organizations (RBOs), Transfrontier Conservation Areas (TFCAs), development partners, civil society, International Cooperating Partners (ICPs), and financial institutions for the inaugural Transboundary Water and Landscapes Sustainable Finance Bootcamp.

/ Southern Africa
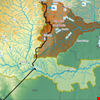
Mozambique and Zimbabwe commit to tackling escalating challenges in the Buzi, Pungwe, and Save River Basins
The governments of Mozambique and Zimbabwe have pledged their commitment to tackling social, economic, and environmental challenges on the increase in the Buzi, Pungwe, and Save (BUPUSA) River Basins, shared exclusively by the two countries. The commitment was expressed through the signing of the Strategic Action Programme (SAP) for the BUPUSA Watercourses by ministers for water in the two countries, on 29 November 2024. The 10-year SAP was developed by the two governments with funding from the Global Environment Facility (GEF) and technical support from the Global Water Partnership Southern Africa and the International Union for Conservation of Nature.

/ Eastern Africa, Southern Africa
Upcoming event: Pan-Africa Water Governance and International Water Law (IWL) Training-9-12 December 2024
Join us for a transformative training designed to foster partnerships and build your expertise in transboundary water law. The 2024 Pan Africa Water Governance and International Water Law (IWL) Training which will be held on 9-12 December 2024 in Entebbe, Uganda in a hybrid format will help participants gain skills and knowledge needed to develop effective agreements and promote stronger cooperation over shared water resources across Africa.

/ Southern Africa
Accelerating Transboundary Water Projects: Bridging Funding and Capacity Gaps
Robust transboundary water management systems are pivotal to mobilizing investments into water projects for economic growth, regional integration, and resilience to climate change.

/ Southern Africa
Angola & Namibia kickstart implementation of joint transboundary water project to strengthen water security
The governments of Angola and Namibia have officially endorsed and kickstarted the implementation of a joint transboundary water project titled "Enhanced Water Security and Community Resilience in the Adjacent Cuvelai and Kunene Transboundary River Basins." This initiative aims to address the pressing challenges of water scarcity, floods, and droughts in the Cuvelai and Kunene River Basins.

/ Southern Africa
Flowing Towards Harmony: Using Transboundary Water Cooperation for Peace in Southern Africa
Growing populations and climatic impacts are placing unprecedented pressure on water resources. This is true of the Southern African Development Community (SADC) region which comprises 16 Member States, whose population in 2018, was estimated to be at 345.2 million, a rise from 336.9 million as of 2017. Rivers play a pivotal role in the region's socio-economic development, as evidenced by its reliance on these waterways. Southern Africa boasts of 15 major transboundary river basins, shared among neighbouring countries, with 13 basins entirely within the region's borders. However, the equitable distribution of water resources remains a challenge, exacerbated by climatic factors influencing rainfall patterns and the geographical distribution of river basins. While these rivers can spark conflicts, they also serve as conduits for peace and cooperation. Therefore, prioritizing transboundary water cooperation is not merely about economic prosperity but also essential for nurturing stability and harmony throughout the region.

/ Southern Africa
SADC and partners to discuss inclusive water resources management at the 10th SADC River Basin Organizations Workshop
The Southern African Development Community (SADC), in collaboration with the Limpopo Watercourse Commission (LIMCOM), and with the technical support of the Global Water Partnership Southern Africa (GWPSA), is scheduled to convene the 10th SADC River Basin Organisations / Shared Watercourse Institutions (RBOs/SWIs) Workshop on 2-4 October 2023.