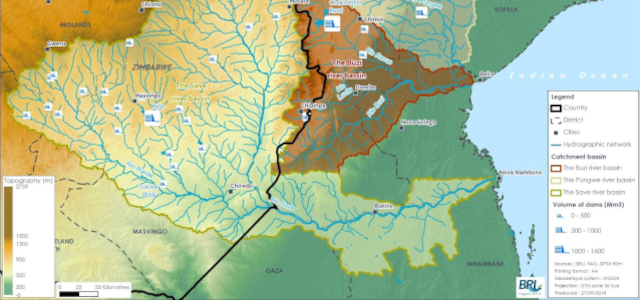
Map of the BUPUSA River Basins, exclusively shared by Mozambique and Zimbabwe. Photo Credit: GEF BUPUSA project
Mozambique and Zimbabwe share at least five river basins, namely Limpopo, Zambezi, Pungwe, Buzi, and Save. The last three basins, collectively known as BUPUSA, are exclusively shared by the two countries. Water resources planning, development, and sustainable management of projects in the BUPUSA basins rely on cooperation between the two countries. With funding from the Global Environment Facility (GEF), Global Water Partnership Southern Africa (GWPSA) is supporting the two governments in strengthening transboundary water management within the basins, through the Management of Competing Water Uses and Associated Ecosystems in Pungwe, Buzi, and Save Basins (GEF-BUPUSA) project, implemented by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
A major step towards achieving this cooperation was the establishment of the Buzi, Pungwe, and Save Watercourse Commission (BUPUSACOM) by the Mozambican and Zimbabwean Governments through the BUPUSA Establishment Agreement, which they signed in May 2023. The Commission, launched in July 2023, consists of four organs, which are the Council of Ministers, the Technical Committee, the Taskforce Teams, and the Secretariat.
The Council of Ministers, comprising the Ministers responsible for water resources from the two governments, is the supreme decision-making body of the Commission.
The Technical Committee, made up of senior officials from the two governments, implements policies and decisions made by the Council and develops strategic plans for the three watercourses for recommendations to the Council for approval. This is done with the technical support of the Secretariat.
The Secretariat, led by an Executive Secretary, is the administrative body of the Commission, responsible for overseeing the planning, development, and management of the water resources within the three River Basins. Member states have already nominated the technical committee.
The BUPUSA Secretariat is currently hosted by the Mozambican Government for the first 15 years as stipulated in the BUPUSA Hosting Agreement of 2023.Thereafter, hosting becomes rotational between the two countries.
Critical to coordinatedcooperation and joint utilization of the water resources in the BUPUSA basins are the water-sharing agreements between the two countries. The Pungwe Water Sharing Agreement was signed in 2016, while the Buzi and Save Accords were signed in 2019 and 2023, respectively.
In the implementation of these water-sharing Agreements, the Commission is governed by the general principles of international water conventions, the Revised SADC Protocol on Shared Watercourses (2000),and national laws and policies in the two Member States. The SADC Protocol calls for the need to establish river basin institutions, such as river basin commissions, joint water commissions, and water-sharing agreements. The Commission also commits to adopting the necessary measures, policies, strategies, programmes, and projects to eliminate discrimination and achieve gender equality and equity.
Land cover map of the Buzi, Pungwe, and Save basins: Photo credit: BRL Engineering
The BUPUSA basins are prone to extreme hydro-metrological events (floods and droughts). Human activities in the basins are also on the rise, causing damage to the environment as well as deteriorating water quality.
GWPSA support was provided to the two governments during the last phase of the negotiations for the Save Water Sharing Agreement and the BUPUSA Establishment and Hosting Agreements, as part of the deliverables for the GEF-BUPUSA project. The project focuses on the conservation, sustainable use, and risk mitigation aspects of the BUPUSA basins’ water resources and the promotion of holistic approaches using the water-energy-food nexus, with a specific interest in connected ecosystems.
In 2019, GWPSA supported the finalisation of the negotiation process that led to the signing of the Buzi agreement through the Buzi, Pungwe, Save Tri-Basin Project under the SADC-GIZ Transboundary Water Management in SADC (GIZ-TWM) Programme, executed by GWPSA on behalf of the SADC Secretariat.
To view this article in Portuguese, click here.